|
Airway management is a commonly discussed topic in emergency medicine and there are some challenges that are unique with trauma. Mike Sharma co-hosts again with our ATLS podcast series on this topic. Take the time to listen both to better prepare for your ATLS course but also to better manage your future trauma patients.
As always, there is a ton of content in these podcasts so make sure to listen to the actual podcast. Here are some of the highlights from what was discussed in the podcast.
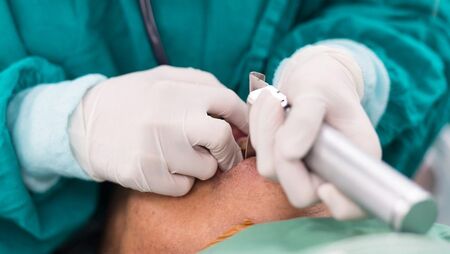
Strongly consider (although ATLS says "must") administering oxygen in trauma patients. The first steps toward identifying and managing potentially life-threatening airway compromise are to recognize objective signs of airway obstruction and identify any trauma or burn involving the face, neck, and larynx. Therefore, the most important early assessment measure is to talk to the patient and stimulate a verbal response. A positive, appropriate verbal response with a clear voice indicates that the patient’s airway is patent, ventilation is intact, and brain perfusion is sufficient. A definitive airway is defined as a tube placed in the trachea with the cuff inflated below the vocal cords, the tube connected to a form of oxygen-enriched assisted ventilation, and the airway secured in place with an appropriate stabilizing method. Unless they’re just going to die on the table, all trauma patients must be moved. Securing any adjuncts is critical, especially the airway. Commercial devices are superior to rigging with tape. It will help avoid issues with skin breakdown over the long term and endotracheal tube dislodgement. Maintaining oxygenation and preventing hypercarbia are critical in managing trauma patients, especially those who have sustained head injuries. Consider prophylactic intubation or early intubation in trauma patients, especially with burns. If intubation is unsuccessful (in a patient with laryngeal trauma), an emergency tracheostomy is indicated, followed by operative repair. However, a tracheostomy is difficult to perform under emergency conditions, can be associated with profuse bleeding, and can be time-consuming. Surgical cricothyroidotomy, although not preferred in this situation, can be a lifesaving option. Most of those working in the trauma environment will be more familiar with and only comfortable with perform a cricothyroidotomy versus a tracheostomy. This is a good time to remember the concept of CICO (Can't Intubate, Can't Oxygenate) which we covered very early on with the Vortex podcast. When a patient is not able to be intubated and oxygenation is not possible otherwise, a surgical airway is then placed as described. Abusive and belligerent patients may in fact be hypoxic; do not assume intoxication. This has also been mentioned in the excited delirium podcast that we previously covered. Ensuring a patent airway is only the first step when providing oxygenation to patients. A patent airway benefits a patient only when ventilation is also adequate. Therefore, clinicians must look for any objective signs of inadequate ventilation. Objective signs of inadequate ventilation: 1. Look for symmetrical rise and fall of the chest and adequate chest wall excursion. 2. Listen for movement of air on both sides of the chest. 3. Use a pulse oximeter to measure the patient’s oxygen saturation and gauge peripheral perfusion. Note, however, that this device does not measure the adequacy of ventilation. 4. Use capnography in spontaneously breathing and intubated patients to assess whether ventilation is adequate. Capnography may also be used in intubated patients to confirm the tube is positioned within the airway. Colorimeter cannot detect hypercarbia. Patients with a Glasgow Coma Scale of 8 or less or who have apnea require prompt intubation! Any trauma patient potentially require immobilization of the cervical spine which can make airway management even more challenging. Using a hyperangulated video laryngoscope can help avoid excess movement compared to standard geometry blades. Supraglottic airway devices can be used but are not definitive airways and should be replaced with a definitive airway device as soon as possible. When possible, use a device that can be intubated through (able to place an tracheal tube introducer [bougie] through the device and into the trachea). When managing the airway, make sure to address HOp killers (Hemodynamics, Oxygenation, and pH [acidosis]) which has been covered in our Resuscitate Then Intubate (RTI) podcast. Patients with GCS scores of 8 or less require prompt intubation! If the patient is moved, reassess tube placement with auscultation of both lateral lung fields for equality of breath sounds and by reassessment for exhaled CO2. Drug-assisted intubation is indicated in patients who need airway control, but have intact gag reflexes, especially in patients who have sustained head injuries. Because of the potential for severe hyperkalemia, succinylcholine must be used cautiously in patients with severe crush injuries, major burns, and electrical injuries. Extreme caution is warranted in patients with preexisting chronic renal failure, chronic paralysis, and chronic neuromuscular disease. Care must be taken, especially with children, to avoid damage to the cricoid cartilage, which is the only circumferential support for the upper trachea. For this reason, surgical cricothyroidotomy is not recommended for children under 12 years of age. Every effort should be made to optimize intubation conditions to ensure success on the first attempt. One great resource is the Kovacs Kata from EmCrit. Let us know what you think by giving us feedback here in the comments section or contacting us on Twitter or Facebook. Remember to look us up on Libsyn and on Apple Podcasts. If you have any questions you can also comment below, email at [email protected], or send a message from the page. We hope to talk to everyone again soon. Until then, continue to provide total care everywhere.
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
Libsyn and iTunesWe are now on Libsyn and iTunes for your listening pleasure! Archives
August 2022
Categories |
||||||

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed